Voice in speech refers to the unique characteristics of sound that are produced by the human vocal apparatus. It includes factors such as pitch, volume, and tone, which play a crucial role in conveying meaning and emotions during communication. Understanding the science behind voice in speech can help us appreciate the intricacies of human communication and the ways in which it can be influenced by various factors. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of voice in speech, exploring the different elements that contribute to its unique qualities and how they can impact our perception of language.
What is Voice in Speech?
The Definition of Voice
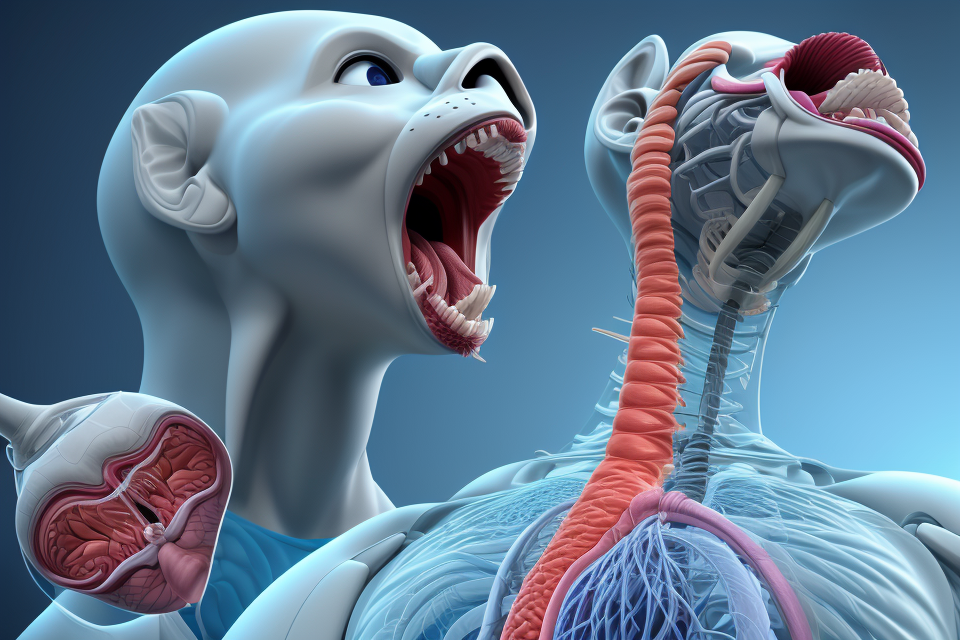
Voice is a sound that is produced by the vibration of the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx. It is the means by which we communicate our thoughts, ideas, and emotions to others. The voice is a complex phenomenon that involves not only the vocal cords but also the resonance of the vocal tract, including the mouth, nose, and throat.
In speech, the voice is used to convey not only the content of the message but also its emotional and social significance. Different types of voices can be used for different purposes, such as a soft voice for intimate conversations or a loud voice for public speaking.
Moreover, the voice is an essential aspect of nonverbal communication, which can convey a wide range of information about a person’s emotions, attitudes, and social status. Therefore, understanding the science behind voice in speech is crucial for effective communication and social interaction.
The Importance of Voice in Communication
Voice in speech refers to the sound produced by a person’s vocal cords and resonated through the throat, mouth, and nose. It is a critical component of human communication, and understanding its importance can shed light on how it affects our interactions with others.
Nonverbal Communication
Voice is a significant aspect of nonverbal communication, which plays a crucial role in conveying emotions, attitudes, and intentions. Through the tone, pitch, and volume of our voice, we can express feelings such as happiness, sadness, anger, or fear. These nonverbal cues are often more influential than the words themselves, and they can greatly impact how our message is perceived by others.
Emotional Influence
Voice is also a powerful tool for expressing emotions and conveying empathy. Our tone of voice can signal to others whether we are happy, sad, angry, or afraid, and it can also convey emotional support or criticism. For example, a gentle and caring tone can comfort a friend in distress, while a stern tone can indicate disapproval or disapproval.
Credibility and Trustworthiness
The quality of our voice can also influence how credible and trustworthy we appear to others. A strong, confident voice can project authority and competence, while a weak or trembling voice may signal insecurity or uncertainty. Therefore, paying attention to the quality of our voice can help us build trust and establish our credibility in various social situations.
Cultural Differences
Finally, it is important to note that the importance of voice in communication can vary across cultures. For example, in some cultures, a loud or assertive voice may be seen as a sign of strength and confidence, while in others, a soft or submissive voice may be preferred. Understanding these cultural differences can help us communicate more effectively and avoid misunderstandings in cross-cultural interactions.
The Different Elements of Voice
When we speak, our voice is the sound that emerges from our mouths. But what makes up our voice? There are several elements that contribute to the sound of our voice, including:
- Pitch: This refers to the highness or lowness of a sound. In speech, pitch is primarily determined by the vibration of the vocal cords.
- Intensity: This refers to the loudness or softness of a sound. In speech, intensity is determined by the amount of air that is expelled from the lungs.
- Quality: This refers to the timbre or tone of a sound. In speech, quality is determined by the shape and tension of the vocal cords.
- Articulation: This refers to the way sounds are shaped and modified by the tongue, lips, and other parts of the mouth. In speech, articulation is responsible for the distinct sounds of words and the way they are pronounced.
Understanding these different elements of voice is important for speech therapists, linguists, and other researchers who study speech and communication. By analyzing the different components of voice, they can gain insights into how speech is produced and how it may be affected by various factors, such as age, language background, and health conditions.
Understanding the Physiology of Voice
The Anatomy of the Vocal Tract
The vocal tract is the passageway that runs from the larynx to the lips, and it is responsible for producing sound when we speak. The vocal tract is made up of several components, including the larynx, pharynx, and mouth.
- Larynx: The larynx, also known as the voice box, is located at the top of the trachea in the neck. It contains two pairs of vocal cords, which are responsible for producing sound when we speak.
- Pharynx: The pharynx is a muscular tube that connects the back of the nasal cavity to the esophagus. It serves as a passageway for air, food, and liquids.
- Mouth: The mouth is the opening through which we speak and eat. It contains the teeth, tongue, and lips, which are all important for producing sound when we speak.
Understanding the anatomy of the vocal tract is essential for understanding how we produce sound when we speak. The position and movement of the vocal cords, the shape of the mouth and lips, and the movement of the tongue are all critical factors that contribute to the production of sound.
The Mechanics of Phonation
When we speak, our vocal cords vibrate to produce sound. This process, known as phonation, is a complex interaction between the air we breathe and the muscles and tissues of the larynx.
- The Larynx:
- The larynx, also known as the voice box, is located at the top of the trachea in the neck.
- It contains two main sections: the supraglottis, which is above the vocal cords, and the subglottis, which is below them.
- The larynx is surrounded by muscles that help to control the flow of air and the vibration of the vocal cords.
- The Vocal Cords:
- The vocal cords are two bands of tissue that are located in the larynx, one on each side of the trachea.
- They are about the size of a pencil eraser and are made up of connective tissue and muscle fibers.
- When air passes through the larynx, the vocal cords vibrate and produce sound.
- The Mechanics of Phonation:
- Phonation occurs when air from the lungs is passed through the larynx and causes the vocal cords to vibrate.
- The vibration of the vocal cords creates sound waves that are amplified by the resonating cavities of the throat and mouth.
- The pitch and quality of the sound are determined by the tension and position of the vocal cords, as well as the shape and size of the resonating cavities.
- When we speak, the muscles in the larynx and throat work together to control the airflow and vibration of the vocal cords, allowing us to produce a wide range of sounds and speech patterns.
The Role of Resonance in Voice
Resonance is a key aspect of voice production that plays a crucial role in shaping the quality and character of an individual’s voice. It refers to the reinforcement and amplification of sound waves that occurs when they resonate within the vocal tract, including the vocal cords, the pharynx, the mouth, and the nasal cavities. This resonance gives the voice its unique timbre and helps to project it effectively.
The human voice is a complex mixture of sound waves that is produced by the vibration of the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx. The sound waves then pass through the pharynx and into the mouth, where they are shaped and modified by the oral cavity. The resonance of these sound waves is enhanced by the dimensions and shape of the oral cavity, as well as the position and movement of the tongue, lips, and jaw.
Resonance is also influenced by the position of the larynx, which can move up and down in the neck. When the larynx is higher in the neck, the vocal cords are shorter, and the voice has a higher pitch. Conversely, when the larynx is lower in the neck, the vocal cords are longer, and the voice has a lower pitch.
In addition to its role in shaping the quality and character of the voice, resonance also plays a critical role in voice projection. When sound waves resonate within the vocal tract, they are amplified and reinforced, allowing the voice to be projected more effectively. This is why people with a deeper voice tend to have a more projected voice, as the resonance of the sound waves is enhanced by the larger dimensions of their oral cavity.
Overall, the role of resonance in voice production is complex and multifaceted, and it plays a critical role in shaping the quality, character, and projection of an individual’s voice. Understanding the mechanisms of resonance can help singers, public speakers, and other voice professionals to optimize their vocal production and achieve their desired sound.
The Importance of Breath Control in Voice Production
In order to produce a clear and powerful voice, it is essential to understand the physiology of voice production. One of the most critical components of voice production is breath control. Breath control is the ability to control the rate, volume, and pattern of breathing in order to produce a specific sound or tone.
When we speak, air from our lungs is pushed through the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx. The vocal cords vibrate as the air passes through them, producing sound. The pitch and tone of the sound are determined by the tension and movement of the vocal cords.
Breath control is crucial because it affects the amount of air that is available to vibrate the vocal cords. If there is not enough air, the vocal cords will not be able to vibrate properly, resulting in a weak or strained sound. On the other hand, if there is too much air, the vocal cords may vibrate too much, resulting in a breathy or airy sound.
Therefore, breath control is an essential aspect of voice production. By learning to control our breathing, we can produce a clearer, more powerful voice.
The Psychology of Voice
The Connection Between Voice and Emotion
Voice is an integral part of human communication, and it is closely linked to our emotions. The way we speak, the tone of our voice, and the words we choose can all convey our emotions to others. In fact, research has shown that our voice can even influence our own emotions.
One of the most well-known examples of the connection between voice and emotion is the concept of “vocal tonality.” This refers to the pattern of pitch, volume, and intensity that we use when speaking. Different vocal tonality patterns can convey different emotions, such as happiness, sadness, anger, or fear. For example, a person who is feeling happy may speak in a higher pitch with more volume and intensity, while a person who is feeling sad may speak in a lower pitch with less volume and intensity.
Another aspect of the connection between voice and emotion is the role of nonverbal cues. Nonverbal cues, such as facial expressions and body language, can also convey emotions to others. For example, a person who is feeling happy may smile and use more open body language, while a person who is feeling sad may frown and use more closed body language.
The connection between voice and emotion is also important in therapeutic settings. Speech-language pathologists and other healthcare professionals often use voice analysis to help patients who are struggling with emotional or psychological issues. By analyzing a patient’s voice, these professionals can gain insight into the patient’s emotional state and develop strategies to help them manage their emotions more effectively.
Overall, the connection between voice and emotion is a complex and multifaceted aspect of human communication. By understanding this connection, we can better understand how our emotions influence our communication and develop strategies to improve our emotional well-being.
The Impact of Voice on Perception and Social Interaction
The way we perceive and interpret voices plays a significant role in our social interactions. The following factors contribute to the impact of voice on perception and social interaction:
- Emotional Expression: Our voices convey emotions that help us communicate our feelings to others. For example, a higher pitch may indicate excitement or nervousness, while a lower pitch may signify confidence or aggression. These emotional expressions can influence how others perceive us and can shape social interactions.
- Personality Traits: The characteristics of our voices, such as volume, tone, and pace, can reveal aspects of our personality. For instance, a louder voice may suggest assertiveness, while a softer voice may indicate timidity. People’s perceptions of our personalities based on our voices can impact social interactions and relationships.
- Gender and Cultural Norms: In many cultures, gender is associated with specific vocal characteristics. For example, traditionally, a higher-pitched voice is often linked to femininity, while a lower-pitched voice is associated with masculinity. People’s expectations of appropriate vocal behavior based on gender and cultural norms can influence how they perceive and interact with others.
- Attractiveness and Vocal Attractiveness: Research has shown that people are more likely to find voices they perceive as attractive to be coming from physically attractive individuals. This phenomenon, known as “vocal attractiveness,” can influence how people perceive and interact with others in social situations.
- Familiarity and Trust: The voice of a familiar person can elicit feelings of trust and comfort, while an unfamiliar voice may arouse suspicion or anxiety. Familiarity with a person’s voice can play a role in the establishment and maintenance of social relationships.
- Nonverbal Communication: The way we use our voices goes beyond the words we speak. Silence, pauses, and the rhythm of our speech can convey important information about our thoughts and feelings. Our voices also provide cues to our listeners about when to speak and when to listen, influencing the flow of social interactions.
These factors demonstrate the complex interplay between voice and perception in social interactions. Understanding the psychology of voice can help us navigate and improve our communication with others.
The Role of Voice in Nonverbal Communication
Voice plays a significant role in nonverbal communication, which refers to the transmission of messages through nonverbal cues such as body language, facial expressions, and tone of voice. The way we speak, including our pitch, volume, and pace, can convey a range of emotions and intentions that may not be explicitly expressed in words.
For example, a soft and hesitant tone of voice may suggest uncertainty or insecurity, while a loud and confident tone may convey authority or dominance. Similarly, a rapid speech pace may indicate excitement or urgency, while a slow and deliberate pace may suggest caution or emphasis.
Moreover, the way we hear and interpret others’ voices is also influenced by our own personal experiences and cultural background. For instance, a person’s accent or dialect may be perceived as friendly or threatening depending on the listener’s own cultural context.
Overall, the role of voice in nonverbal communication is complex and multifaceted, and it is essential to understand how our own voice and the voices of others can influence our perceptions and interactions with others.
The Effects of Voice on Listeners
When we speak, our voice is not just a means of communication but also a tool for expressing emotions and conveying information about our identity. Our voice can reveal our gender, age, and cultural background, and it can influence how others perceive us. But what effect does our voice have on the listeners?
- Voice can convey emotions: Our voice can reveal our emotional state, whether we are happy, sad, angry, or afraid. This is because the tone, pitch, and intensity of our voice can change depending on our emotions. For example, when we are happy, our voice may be more upbeat and enthusiastic, while when we are sad, our voice may be slower and more melancholic.
- Voice can influence perceptions: Our voice can also influence how others perceive us. For example, a person with a deep, authoritative voice may be perceived as more confident and powerful, while a person with a high-pitched, childlike voice may be perceived as more innocent and vulnerable.
- Voice can enhance memory: Our voice can also enhance our memory. For example, when we hear a familiar voice, it can trigger memories of the person associated with that voice. This is because our brain is wired to recognize and remember voices, as they are an important source of social information.
- Voice can improve social bonding: Our voice can also improve social bonding. When we talk to someone, our voice sends social cues that help us connect with the other person. For example, when we talk to a friend, our voice may become more informal and intimate, which can strengthen our bond with that person.
Overall, the effects of voice on listeners are complex and multifaceted. Our voice is not just a means of communication but also a powerful tool for expressing emotions, influencing perceptions, enhancing memory, and improving social bonding.
Voice Disorders and Their Treatment
Common Voice Disorders
- Voice Tremors: An involuntary, rhythmic muscle contraction and relaxation that causes a shaking or trembling of the voice.
- Causes: Neurological disorders, medication side effects, or stress.
- Symptoms: Unstable or unsteady voice quality, difficulty speaking, and shaking of the head or neck while speaking.
- Spasmodic Dysphonia: A disorder that affects the muscles used for speaking, causing them to spasm or tighten involuntarily.
- Causes: Abnormal function of the brain’s basal ganglia, which controls movement.
- Symptoms: Strained or breathy voice, breaks in the voice, and difficulty speaking in a normal tone.
- Vocal Cord Paralysis: A condition where one or both vocal cords do not move properly, affecting voice production.
- Causes: Nerve damage, viral infections, or thyroid issues.
- Symptoms: Weak or hoarse voice, breathy speech, and inability to project the voice.
- Aphonia: A complete loss of voice due to problems with the vocal cords or other structures in the voice production process.
- Causes: Vocal cord paralysis, laryngeal cancer, or laryngectomy.
- Symptoms: Complete loss of voice, difficulty speaking, and swallowing issues.
- Vocal Cord Nodules: Growths on the vocal cords that result from overuse or misuse of the voice.
- Causes: Excessive screaming, singing, or talking for extended periods.
- Symptoms: Hoarseness, throat pain, and voice cracks.
- Laryngitis: Inflammation of the vocal cords, usually caused by viral infections or overuse.
- Causes: Viral infections, acid reflux, or excessive talking or singing.
- Symptoms: Hoarseness, loss of voice, and discomfort in the throat.
- Polyps or nodules on the vocal cords: Abnormal growths that can interfere with voice production.
- Causes: Long-term smoking, excessive use of the voice, or acid reflux.
- Symptoms: Hoarseness, loss of voice, and difficulty speaking.
Diagnosis and Assessment of Voice Disorders
The diagnosis and assessment of voice disorders is a crucial step in determining the appropriate treatment plan for an individual. A thorough evaluation is necessary to identify the underlying cause of the voice disorder and to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the problem.
There are several methods that are commonly used to diagnose and assess voice disorders. One of the most common methods is a thorough medical history and physical examination. During this examination, the healthcare provider will ask questions about the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and lifestyle habits. They will also perform a visual examination of the vocal cords using a specialized instrument called a laryngoscope.
Another common method of diagnosis is the use of specialized tests, such as acoustic analysis, videostroboscopy, and laryngoscopy. Acoustic analysis involves measuring the characteristics of the individual’s voice, such as pitch, loudness, and quality. Videostroboscopy involves the use of a strobe light to visualize the movement of the vocal cords during speech. Laryngoscopy involves the use of a mirror or a specialized instrument to view the vocal cords directly.
In addition to these methods, voice therapy may also be recommended as a part of the diagnosis and assessment process. Voice therapy is a type of therapy that is specifically designed to improve the function of the vocal cords and to treat voice disorders. It may involve exercises to improve breath control, articulation, and resonance, as well as techniques to reduce strain on the vocal cords.
Overall, the diagnosis and assessment of voice disorders is a complex process that requires a thorough evaluation of the individual’s symptoms, medical history, and vocal function. By using a combination of methods, including medical history and physical examination, specialized tests, and voice therapy, healthcare providers can accurately diagnose and assess voice disorders and develop an appropriate treatment plan for each individual.
Treatment Options for Voice Disorders
When it comes to treating voice disorders, there are several options available. The choice of treatment will depend on the specific type of disorder and its severity. Here are some of the most common treatment options:
Voice Therapy
One of the most common treatments for voice disorders is voice therapy. This involves working with a speech-language pathologist (SLP) to learn exercises that can help strengthen and improve the voice. The SLP will teach techniques such as breathing exercises, vocal warm-ups, and posture adjustments to help improve the quality and function of the voice.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help treat voice disorders. For example, anti-inflammatory medications may be used to reduce inflammation in the vocal cords, while muscle relaxants may be used to help relax the vocal cords and reduce tension.
Surgery
In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to treat a voice disorder. Surgery may be used to remove polyps or nodules from the vocal cords, or to repair a vocal cord paralysis. However, surgery is typically only recommended when other treatments have been unsuccessful.
Lifestyle Changes
In some cases, making lifestyle changes can help improve voice function. For example, avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can help reduce inflammation in the vocal cords. Avoiding excessive use of the voice, such as talking for long periods of time or speaking loudly, can also help prevent damage to the vocal cords.
Overall, the choice of treatment for a voice disorder will depend on the specific type of disorder and its severity. In many cases, a combination of treatments may be used to achieve the best results. It is important to work closely with an SLP or other healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Preventing Voice Disorders
Maintaining a healthy voice is crucial for individuals who rely on their voices for communication, such as professional singers, actors, and public speakers. Here are some practical tips for preventing voice disorders:
- Hydration: Staying well-hydrated is essential for maintaining a healthy voice. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding caffeine and alcohol can help prevent dehydration, which can lead to vocal strain and damage.
- Warm-up exercises: Engaging in warm-up exercises before using your voice can help prevent injury. Gentle exercises such as humming, lip trills, and diaphragmatic breathing can help prepare the voice for use.
- Posture: Maintaining good posture is crucial for proper breathing and voice production. Standing or sitting up straight with the shoulders relaxed and the chest open can help promote proper breathing and prevent tension in the neck and throat.
- Avoiding excessive use: Overusing the voice can lead to strain and injury. Taking breaks when necessary, avoiding prolonged use of the voice, and limiting talking in noisy environments can help prevent voice disorders.
- Proper nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can help maintain a healthy voice. Incorporating foods that are rich in vitamins A, C, and E, which are essential for voice production, can help keep the voice healthy.
- Avoiding irritants: Avoiding exposure to irritants such as smoke, dust, and pollution can help prevent voice disorders. Using a humidifier or saline nasal spray can also help moisten the airways and prevent dryness.
- Seeking treatment early: If you experience any changes in your voice or notice any discomfort, it is essential to seek medical attention promptly. Early intervention can prevent voice disorders from worsening and lead to more effective treatment.
Applications of Voice Science in Different Fields
Voice in Singing and Acting
The application of voice science in singing and acting is vast and multifaceted. Understanding the science behind voice production is crucial for singers and actors to achieve their desired sound and performance. Here are some ways in which voice science is used in these fields:
Anatomy and Physiology of Singing
Singing involves the use of the vocal cords, which are located in the larynx. The vocal cords vibrate to produce sound, and the pitch and volume of the sound are determined by the vibration of the cords. Voice science teaches singers how to use their vocal cords to produce different sounds and control their tone. Singers also need to understand the role of the diaphragm, the muscles used in breathing, and the resonators in the throat and chest to produce a good quality sound.
Vocal Health and Maintenance
Singing can be physically demanding and can cause damage to the vocal cords if not done correctly. Voice science helps singers understand how to maintain good vocal health. Singers need to warm up their voices before performing, hydrate, and avoid excessive use of their voices. Voice science also teaches singers how to recognize signs of vocal strain or damage and when to seek medical attention.
Articulation and Pronunciation
Actors also rely on voice science to help them pronounce words correctly and project their voices. The science of voice production helps actors understand the mechanics of speech and how the voice is produced. This knowledge helps actors to pronounce words clearly and project their voices without straining them.
Vocal Emotion and Expression
Actors also use voice science to convey emotion and create character. Voice science teaches actors how to manipulate their voices to convey different emotions and moods. Actors can also use voice science to create different characters by altering their vocal qualities, such as pitch, volume, and tone.
In summary, voice science plays a crucial role in singing and acting. Singers and actors use the principles of voice production to control their voices, maintain vocal health, and convey emotion and character. Understanding the science behind voice production is essential for anyone who wants to become a skilled singer or actor.
Voice in Public Speaking and Presentations
Voice science plays a crucial role in public speaking and presentations, enabling speakers to convey their message effectively and engage their audience. By understanding the principles of voice science, public speakers can optimize their vocal performance, improve their presentation skills, and enhance their overall communication effectiveness.
Importance of Voice in Public Speaking
In public speaking, the voice is the primary tool used to convey thoughts, ideas, and emotions to the audience. A clear, confident, and engaging voice can captivate the audience’s attention, while a weak or ineffective voice can lose their interest. Therefore, it is essential for public speakers to understand the science behind voice and apply it to their speaking style.
Factors Affecting Voice in Public Speaking
Several factors can affect the voice in public speaking, including breathing, posture, articulation, and intonation. Proper breathing techniques can help speakers project their voice, maintain tone, and prevent vocal strain. Good posture can facilitate breathing and prevent tension in the vocal cords. Clear articulation and appropriate intonation can enhance the clarity and effectiveness of the message.
Voice Training for Public Speakers
Voice training can be beneficial for public speakers to improve their vocal performance and presentation skills. Professional voice coaches can teach speakers how to breathe correctly, use their vocal cords efficiently, and develop good pronunciation and intonation. Through voice training, public speakers can develop a confident and engaging speaking style that captivates their audience.
Tips for Effective Voice Use in Public Speaking
Here are some tips for effective voice use in public speaking:
- Warm up the voice before speaking to prevent vocal strain and maintain tone.
- Use proper breathing techniques to support the voice and project the message.
- Maintain good posture to facilitate breathing and prevent tension in the vocal cords.
- Practice clear articulation and appropriate intonation to enhance the clarity and effectiveness of the message.
- Use gestures and body language to enhance the message and engage the audience.
- Adapt the speaking style to the audience and the occasion to convey the message effectively.
In conclusion, voice science plays a crucial role in public speaking and presentations. By understanding the principles of voice science and applying them to their speaking style, public speakers can optimize their vocal performance, improve their presentation skills, and enhance their overall communication effectiveness.
Voice in Business and Sales
In the fast-paced world of business and sales, having a strong and effective voice can make all the difference. Voice science can help sales professionals to optimize their voice for maximum impact, by providing insights into how different vocal techniques can influence customer behavior and decision-making.
For example, research has shown that a higher-pitched voice can make a person appear more youthful and less threatening, which can be an advantage in sales situations where building trust and rapport is crucial. On the other hand, a lower-pitched voice can convey confidence and authority, which can be useful in negotiations or when making a persuasive argument.
Additionally, voice science can help sales professionals to identify and address any vocal issues that may be hindering their performance. For instance, if a salesperson has a monotonous or unengaging speaking style, they may be able to improve their effectiveness by incorporating more vocal variety, such as by using inflection, tone, and pauses to emphasize key points.
Overall, by leveraging the insights of voice science, sales professionals can fine-tune their vocal delivery to better connect with customers and achieve their goals.
Voice in Therapy and Counseling
Voice plays a crucial role in therapy and counseling sessions, as it can reveal important information about a person’s emotional and psychological state. By analyzing a client’s voice, therapists and counselors can gain insights into their thoughts, feelings, and behavior patterns. Here are some ways in which voice science is applied in therapy and counseling:
Speech and Language Analysis
One of the most common applications of voice science in therapy and counseling is speech and language analysis. Therapists and counselors can use this technique to identify language patterns that may indicate certain emotional or psychological issues. For example, a person who is experiencing depression may speak in a monotone voice or use passive language. By identifying these patterns, therapists can tailor their approach to better address the client’s needs.
Vocal Quality Analysis
Another application of voice science in therapy and counseling is vocal quality analysis. This technique involves analyzing various aspects of a person’s voice, such as pitch, tone, and rhythm, to gain insights into their emotional state. For example, a person who is anxious may speak in a high-pitched, rapid voice. By identifying these vocal patterns, therapists can help clients manage their anxiety and develop more effective communication skills.
Voice Therapy
Voice therapy is a type of therapy that focuses specifically on the voice. It can be used to treat a variety of voice disorders, such as vocal nodules, vocal cord paralysis, and spasmodic dysphonia. Voice therapy can also be used to help clients with emotional or psychological issues, such as depression or anxiety, to improve their communication skills and enhance their quality of life.
Articulation and Phonology Therapy
Articulation and phonology therapy is another type of therapy that focuses on speech and language development. It can be used to treat a variety of speech and language disorders, such as stuttering, articulation disorders, and phonological processing disorders. By analyzing a client’s speech patterns, therapists can identify areas of difficulty and develop targeted interventions to improve their speech and language skills.
Overall, voice science plays an important role in therapy and counseling, providing therapists and counselors with valuable insights into a client’s emotional and psychological state. By analyzing a client’s voice, therapists can tailor their approach to better meet the client’s needs and help them achieve their goals.
The Future of Voice Science
Current Trends and Developments in Voice Science
Voice science is a rapidly evolving field that is shedding new light on the complex mechanisms that govern human speech. With the help of cutting-edge technologies and advanced research methods, scientists are gaining a deeper understanding of the biological, psychological, and physiological factors that influence our voices. Here are some of the current trends and developments in voice science:
Biomechanics of Speech
One of the most exciting areas of research in voice science is the study of the biomechanics of speech. Scientists are exploring the mechanical processes that underlie human speech production, including the movement of the vocal cords, the shape of the vocal tract, and the function of the respiratory system. By analyzing these factors, researchers hope to develop new methods for diagnosing and treating speech disorders, such as stuttering and dysphonia.
Vocal Emotion Perception
Another important area of research is the study of vocal emotion perception. Scientists are investigating how listeners perceive and interpret the emotional content of speech, and how this information is processed in the brain. By understanding the neural mechanisms that underlie vocal emotion perception, researchers hope to develop new techniques for analyzing and synthesizing emotional speech, with potential applications in fields such as psychology, marketing, and entertainment.
Voice Interface Technology
Finally, there is growing interest in the development of voice interface technology, which enables users to interact with digital devices using their voices. This technology is becoming increasingly ubiquitous, with the widespread adoption of virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant. Researchers are exploring new ways to improve the accuracy and efficiency of voice recognition systems, as well as developing new applications for voice-enabled devices in fields such as healthcare, education, and transportation.
Overall, the future of voice science looks bright, with exciting new developments on the horizon. By continuing to explore the complex mechanisms that govern human speech, scientists hope to unlock new insights into the nature of human communication, and to develop new technologies and therapies that will benefit people around the world.
Potential Applications of Voice Science in Emerging Technologies
The study of voice science has far-reaching implications that extend beyond the realm of speech and language. As technology continues to advance, the potential applications of voice science in emerging technologies are becoming increasingly apparent.
Virtual Reality and Augmented Reality
One area where voice science can play a significant role is in virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) technology. By analyzing the unique characteristics of a person’s voice, such as pitch, tone, and inflection, voice recognition technology can be used to create a more immersive experience for users. For example, in a VR environment, a user’s voice commands can be used to control their avatar’s movements and interactions with the virtual world.
Artificial Intelligence and Chatbots
Another potential application of voice science is in the development of artificial intelligence (AI) and chatbots. By analyzing a person’s voice patterns, AI-powered chatbots can better understand the emotional context of a conversation and respond appropriately. This technology can be used in a variety of industries, from customer service to mental health counseling.
Biometric Security
Voice recognition technology can also be used for biometric security purposes. By analyzing a person’s unique voiceprint, voice science can be used to identify individuals and verify their identity. This technology can be used in a variety of settings, from banking and finance to border control and national security.
Healthcare
Finally, voice science has the potential to revolutionize the healthcare industry. By analyzing a person’s voice patterns, healthcare professionals can gain insight into a patient’s health and well-being. For example, changes in voice patterns can indicate the onset of certain diseases or conditions, such as Parkinson’s disease or depression. Additionally, voice recognition technology can be used to improve patient communication and facilitate telemedicine.
Overall, the potential applications of voice science in emerging technologies are vast and varied. As the field continues to evolve, it is likely that we will see even more innovative uses for this technology in the years to come.
The Impact of Voice Science on Education and Training
The impact of voice science on education and training is significant and far-reaching. By understanding the physiological and psychological factors that contribute to voice production, educators and trainers can develop more effective teaching methods and techniques to help individuals improve their vocal abilities.
Developing Voice Training Programs
One of the primary ways in which voice science is impacting education and training is through the development of voice training programs. These programs are designed to help individuals develop their vocal skills and improve their overall voice quality. By incorporating the latest findings from voice science research, these programs can be tailored to meet the specific needs of each individual, taking into account factors such as vocal range, breath control, and resonance.
Improving Communication Skills
Another way in which voice science is impacting education and training is by improving communication skills. By understanding the mechanics of voice production, individuals can learn how to communicate more effectively, project their voice, and modulate their tone to better convey their message. This is particularly important in professional settings, where clear and effective communication is essential for success.
Enhancing Performing Arts Education
Finally, voice science is also having an impact on performing arts education. By understanding the physiological and psychological factors that contribute to voice production, educators can help students develop their vocal abilities and improve their overall performance. This is particularly important in music education, where developing strong vocal skills is essential for success as a singer or musician.
Overall, the impact of voice science on education and training is significant and far-reaching. By incorporating the latest findings from voice science research, educators and trainers can develop more effective teaching methods and techniques to help individuals improve their vocal abilities and enhance their communication skills.
The Importance of Further Research in Voice Science
The field of voice science is constantly evolving, and there is still much to be discovered about the intricacies of human speech. Further research in this area is essential for a number of reasons.
Firstly, as technology continues to advance, it is becoming increasingly important to understand the mechanics of human speech in order to develop more sophisticated voice recognition systems. These systems are used in a wide range of applications, from virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa to language translation software. By deepening our understanding of the science behind voice, we can improve the accuracy and effectiveness of these systems.
Secondly, there is still much to learn about the ways in which the human voice can be used to convey meaning and emotion. For example, researchers are currently investigating the role of vocal pitch and tone in conveying emotions like anger and sadness. A better understanding of these factors could have implications for fields like psychology and psychiatry, where the ability to accurately interpret nonverbal cues is crucial.
Finally, further research in voice science can help us better understand a range of voice-related disorders, from vocal nodules to Parkinson’s disease. By gaining a deeper understanding of the mechanisms behind these conditions, we can develop more effective treatments and improve the quality of life for those affected.
Overall, the importance of further research in voice science cannot be overstated. As our understanding of the human voice continues to grow, it has the potential to transform a wide range of fields and improve our lives in countless ways.
FAQs
1. What is voice in speech?
Voice in speech refers to the sound produced by the human vocal cords when air is expelled from the lungs and passes through the vocal cords, creating a unique frequency and tone. It is the sound that allows us to communicate and express ourselves through language.
2. What are the components of voice in speech?
The components of voice in speech include pitch, intensity, and tone. Pitch refers to the highness or lowness of the voice, intensity refers to the loudness or softness of the voice, and tone refers to the quality or timbre of the voice.
3. How does the human voice produce sound?
The human voice produces sound through the vibration of the vocal cords. When air is expelled from the lungs, it passes through the vocal cords, causing them to vibrate and produce sound waves. The shape and tension of the vocal cords, as well as the airflow and resonance of the vocal tract, all contribute to the unique sound of each person’s voice.
4. What factors can affect the quality of someone’s voice?
Several factors can affect the quality of someone’s voice, including age, gender, genetics, vocal training, and lifestyle habits such as smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. In addition, factors such as vocal cord injuries, allergies, and acid reflux can also impact the quality and function of the voice.
5. Can voice therapy help improve someone’s voice?
Yes, voice therapy can help improve someone’s voice. Voice therapy is a type of therapy that focuses on improving the function and health of the vocal cords and voice box. It can help individuals with voice disorders, such as vocal cord nodules or paralysis, as well as those with issues related to voice quality, such as breathy or strained speech. Voice therapy typically involves exercises and techniques to improve breath control, vocal cord function, and voice quality.