A hoarse voice is a common symptom that many people experience at some point in their lives. It can be caused by a variety of factors, ranging from minor irritants to serious medical conditions. In this article, we will explore the different causes of a hoarse voice, the symptoms associated with it, and the various treatment options available. We will also discuss when to seek medical attention for a hoarse voice. So, whether you’re a singer, a public speaker, or just someone who wants to understand more about this common symptom, read on to learn more about understanding hoarse voice.
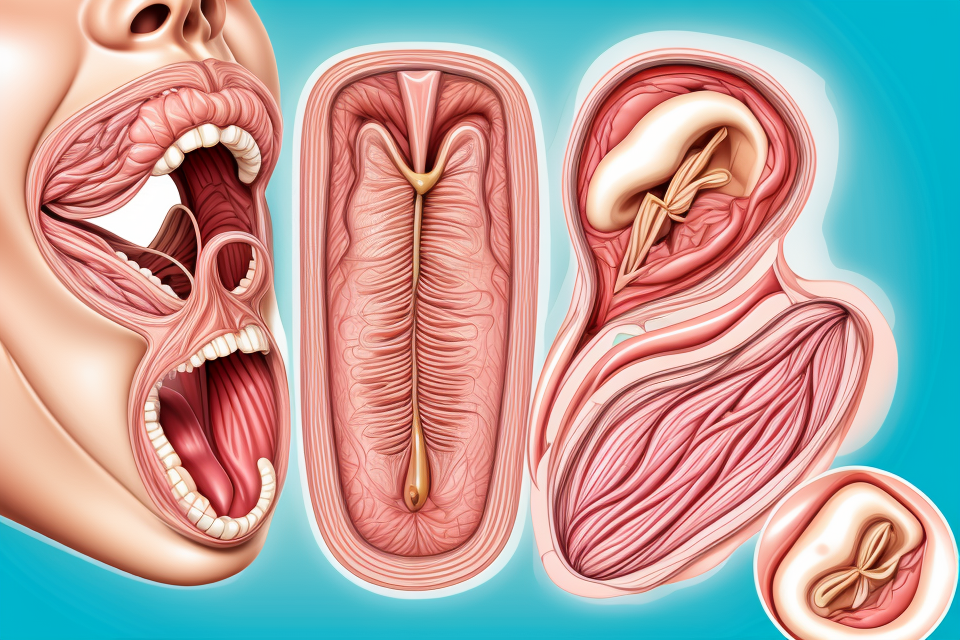
What is a Hoarse Voice?
Definition and Characteristics
A hoarse voice refers to a condition where a person’s voice sounds breathy, raspy, or strained. This is typically due to inflammation or irritation of the vocal cords, which can affect their ability to produce a clear and normal sounding voice. The characteristics of a hoarse voice can vary depending on the underlying cause, but some common symptoms include:
- A raspy or strained quality to the voice
- A decrease in volume or hoarseness when speaking or singing
- A feeling of tightness or discomfort in the throat
- A sore throat or feeling of irritation in the throat
- Difficulty speaking for long periods of time or speaking at a high volume
- A feeling of fatigue or weakness in the voice
It’s important to note that hoarseness can be a symptom of many different conditions, ranging from mild to severe. In some cases, hoarseness may be temporary and resolve on its own, while in other cases it may be a sign of a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention. If you are experiencing hoarseness that persists for more than a few days, it’s important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Causes of Hoarse Voice
A hoarse voice is a condition characterized by a raspy, strained, or breathy quality to the voice. It occurs when the vocal cords become inflamed, irritated, or swollen, leading to changes in the way they vibrate and produce sound. The following are some of the most common causes of a hoarse voice:
Inflammation of the vocal cords
Inflammation of the vocal cords, also known as laryngitis, is one of the most common causes of a hoarse voice. This condition occurs when the vocal cords become swollen or irritated, resulting in changes to the way they vibrate and produce sound. Laryngitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral infections, allergies, smoking, and excessive use of the voice.
Vocal cord nodules
Vocal cord nodules, also known as singer’s nodules or nodules of the vocal cords, are small, callous-like growths that can develop on the vocal cords. These nodules can cause a hoarse voice by disrupting the normal vibration of the vocal cords. Vocal cord nodules are often caused by prolonged or excessive use of the voice, such as singing or speaking for long periods of time.
Acid reflux
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), is a condition in which stomach contents, including acid, flow back up into the esophagus. This can irritate the vocal cords and cause a hoarse voice. In some cases, acid reflux may be accompanied by other symptoms, such as heartburn and regurgitation.
Thyroid disease
Thyroid disease, which is a condition that affects the thyroid gland, can also cause a hoarse voice. The thyroid gland is located in the neck and plays a role in regulating metabolism and growth. When the thyroid gland is not functioning properly, it can affect the production of hormones that control the growth and function of the vocal cords, leading to changes in the voice.
Smoking
Smoking is a well-known risk factor for a variety of health conditions, including lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory illnesses. It can also cause a hoarse voice by irritating the vocal cords and leading to inflammation. Smoking can also reduce blood flow to the vocal cords, making them less resilient and more prone to injury.
In summary, a hoarse voice can be caused by a variety of factors, including inflammation of the vocal cords, vocal cord nodules, acid reflux, thyroid disease, and smoking. If you are experiencing hoarseness that persists for several weeks or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Symptoms of Hoarse Voice
Mild to Severe Hoarseness
When discussing the symptoms of a hoarse voice, it is important to note that the severity of the hoarseness can vary from person to person. The following are some of the different levels of hoarseness that an individual may experience:
- Mild Hoarseness: This is typically characterized by a slight raspy or strained quality to the voice. It may be noticeable to others, but the individual is still able to speak normally and perform their daily activities without difficulty.
- Moderate Hoarseness: This level of hoarseness is more pronounced than mild hoarseness and may cause the individual to sound like they have a cold or sore throat. They may have difficulty speaking for long periods of time and may experience a decrease in the volume of their voice.
- Severe Hoarseness: At this level, the individual’s voice may be very hoarse, raspy, or even silent. They may have difficulty speaking and may experience pain or discomfort when attempting to talk. Severe hoarseness can be a sign of a more serious underlying condition and requires medical attention.
It is important to note that hoarseness can be caused by a variety of factors, including vocal strain, laryngitis, nodules, and other conditions. If you are experiencing hoarseness, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and appropriate treatment.
Duration of Hoarse Voice
The duration of hoarse voice can vary depending on the underlying cause. In some cases, hoarseness may be temporary and resolve on its own within a few days to a week. However, in other cases, hoarseness may persist for several weeks or even months.
Factors that can influence the duration of hoarse voice include:
- The severity of the underlying condition causing the hoarseness
- The individual’s age and overall health
- Whether or not the individual is experiencing any complications related to the hoarseness
It is important to note that hoarseness that persists for an extended period of time may indicate an underlying condition that requires medical attention. If you are experiencing hoarseness that has lasted for several weeks or longer, it is recommended that you consult with a healthcare professional for further evaluation and treatment.
Associated Symptoms
Hoarse voice is often accompanied by other symptoms that can help identify the underlying cause. These associated symptoms may include:
- Dry throat: A feeling of dryness or roughness in the throat is a common symptom of hoarse voice. This can be caused by dehydration, allergies, or irritants such as smoke or pollution.
- Cough: A persistent cough can be a sign of an underlying respiratory condition such as bronchitis or pneumonia, which can cause hoarseness.
- Difficulty swallowing: Hoarseness can make it difficult to swallow food or liquid, especially if the vocal cords are inflamed or irritated.
- Pain or discomfort: Hoarseness can also be accompanied by pain or discomfort in the throat, which may be a sign of an underlying condition such as acid reflux or a thyroid disorder.
- Fatigue: People with hoarse voice may also feel fatigued or experience a loss of energy, which can affect their daily activities and quality of life.
It is important to note that while these associated symptoms can help identify the underlying cause of hoarseness, they may also be caused by other conditions. Therefore, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Diagnosis of Hoarse Voice
Physical Examination
A physical examination is a crucial part of diagnosing hoarse voice. The healthcare provider will start by examining the patient’s vocal cords using a scope called a laryngoscope. This scope is inserted through the patient’s nose or mouth to allow the healthcare provider to view the vocal cords. The provider will check for any swelling, redness, or inflammation of the vocal cords.
Additionally, the healthcare provider may ask the patient to perform a series of voice tests to evaluate the severity of the hoarseness and identify any underlying issues. These tests may include:
- Voice Projection Test: The patient is asked to speak in a loud voice and then gradually lower the volume while maintaining good vocal technique.
- Tremor Test: The patient is asked to say “mmm” or “ahh” while the healthcare provider observes the vocal cords for any involuntary movements or tremors.
- Supraglottitis Test: The patient is asked to say “ahh” and the healthcare provider will listen for any crackling or hissing sounds that may indicate inflammation or irritation in the supraglottis.
The physical examination may also include a review of the patient’s medical history, including any recent illnesses, medications, or exposure to irritants that may be contributing to the hoarseness. Based on the results of the physical examination and voice tests, the healthcare provider can determine the appropriate course of treatment for the patient’s hoarse voice.
Diagnostic Tests
In order to determine the underlying cause of a hoarse voice, a healthcare professional may recommend diagnostic tests. These tests can help to identify any structural abnormalities or underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to the hoarseness. Some common diagnostic tests used to diagnose hoarse voice include:
- Laryngoscopy: A laryngoscopy is a diagnostic procedure that involves the use of a small, flexible camera to examine the larynx and vocal cords. This test can help to identify any abnormalities or injuries to the vocal cords that may be causing hoarseness.
- Stroboscopy: A stroboscopy is a diagnostic procedure that uses a strobe light to examine the vocal cords in motion. This test can help to identify any abnormalities in the vibration of the vocal cords that may be contributing to hoarseness.
- Acoustic analysis: An acoustic analysis is a diagnostic test that uses specialized equipment to measure the sound of the voice. This test can help to identify any abnormalities in the sound of the voice that may be contributing to hoarseness.
- Blood tests: In some cases, blood tests may be recommended to rule out any underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to hoarseness, such as thyroid disorders or autoimmune disorders.
It is important to note that these diagnostic tests are typically only necessary if the hoarseness persists for an extended period of time or if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as pain or difficulty swallowing. If you are experiencing hoarseness, it is important to speak with a healthcare professional to determine the underlying cause and to receive appropriate treatment.
Importance of Accurate Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of hoarse voice is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of complications. An incorrect diagnosis can lead to inappropriate treatment, which may worsen the condition or cause harm to the patient.
Several factors can influence the accuracy of the diagnosis, including the severity and duration of the hoarse voice, underlying medical conditions, and the presence of other symptoms. Therefore, it is essential to seek medical advice from a qualified healthcare professional who has experience in diagnosing and treating voice disorders.
The healthcare professional will begin by obtaining a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination to assess the patient’s vocal cords and surrounding structures. In some cases, additional diagnostic tests, such as laryngoscopy, may be required to visualize the vocal cords and identify any abnormalities.
Proper diagnosis of hoarse voice requires a thorough evaluation of all possible causes, including vocal overuse, acid reflux, infections, and underlying medical conditions such as thyroid disorders or laryngeal cancer. A comprehensive diagnosis ensures that the appropriate treatment plan is implemented, which can help alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and promote optimal vocal health.
Treatment of Hoarse Voice
Self-Care Measures
Managing a hoarse voice can often be done through self-care measures. These steps are generally simple and easy to implement at home, and they may help alleviate some of the discomfort associated with a hoarse voice. Some self-care measures for hoarse voice include:
- Resting the Voice: One of the most important self-care measures for a hoarse voice is rest. Overusing the voice can make the condition worse, so it’s essential to give the voice a break when possible. This may involve limiting speaking time, avoiding noisy environments, and being mindful of vocal use during activities such as singing or public speaking.
- Hydration: Staying hydrated is essential for overall health, and it can also help alleviate hoarseness. Drinking plenty of water and other fluids can help keep the vocal cords moist, which can reduce irritation and inflammation. Avoiding alcohol, caffeine, and carbonated beverages can also help maintain vocal health.
- Avoiding Irritants: Exposure to irritants such as smoke, dust, and pollution can dry out the vocal cords and exacerbate hoarseness. Minimizing exposure to these irritants can help reduce symptoms. This may involve avoiding smoky environments, using air purifiers, and wearing protective gear such as masks.
- Posture: Maintaining good posture can help prevent hoarseness by reducing strain on the vocal cords. This may involve sitting up straight, avoiding slouching, and keeping the head and neck in a neutral position.
- Warm-Up and Cool-Down Exercises: Engaging in warm-up and cool-down exercises can help prevent hoarseness by increasing blood flow to the vocal cords and promoting flexibility. This may involve engaging in activities such as humming, singing, or doing simple vocal exercises.
Overall, self-care measures can be an effective way to manage hoarseness and prevent it from becoming a more serious condition. However, if hoarseness persists or worsens, it’s important to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause and receive appropriate treatment.
Medical Treatment
When a hoarse voice is caused by an underlying medical condition, such as a cold or laryngitis, medical treatment may be necessary to address the underlying cause. Some common medical treatments for hoarse voice include:
- Antibiotics: If hoarse voice is caused by a bacterial infection, such as strep throat, antibiotics may be prescribed to clear the infection.
- Corticosteroids: In some cases, corticosteroids may be used to reduce inflammation in the vocal cords and help restore normal voice function.
- Throat lozenges: Over-the-counter throat lozenges may help soothe a sore throat and relieve hoarseness.
- Voice rest: In some cases, voice rest may be recommended to allow the vocal cords to heal and prevent further damage.
It is important to follow the treatment plan prescribed by a healthcare provider and to seek medical attention if hoarse voice persists or worsens. In some cases, medical treatment may be necessary to address underlying medical conditions that are causing hoarse voice.
Lifestyle Changes
Avoiding Irritants
One of the most effective ways to treat a hoarse voice is to avoid irritants that can aggravate the condition. These irritants include smoke, dust, and pollution, which can all dry out the vocal cords and cause inflammation. It is essential to avoid these irritants as much as possible to prevent further damage to the vocal cords.
Hydration
Staying hydrated is also crucial in the treatment of a hoarse voice. Drinking plenty of water can help to keep the vocal cords lubricated, reducing the severity of hoarseness. It is recommended to drink at least eight glasses of water per day to maintain proper hydration levels.
Resting the Voice
Resting the voice is also an essential part of the treatment process. Overuse or excessive use of the voice can cause hoarseness, and it is essential to give the vocal cords time to heal. Avoiding excessive talking, singing, or shouting can help to reduce the strain on the vocal cords and promote healing.
Posture
Maintaining good posture is also important in the treatment of a hoarse voice. Poor posture can put unnecessary strain on the vocal cords, causing them to become irritated and inflamed. It is essential to sit up straight and avoid slouching, which can put pressure on the neck and throat, leading to hoarseness.
By making these simple lifestyle changes, individuals can help to alleviate the symptoms of a hoarse voice and promote healing.
Prevention of Hoarse Voice
Good Vocal Habits
Proper care and maintenance of your vocal cords can prevent hoarseness and protect your voice. Here are some good vocal habits to practice:
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of water helps to keep your vocal cords well-hydrated and healthy.
- Warm-up: Engaging in vocal warm-up exercises before singing or speaking helps to prepare your vocal cords for use and prevent strain.
- Posture: Maintaining good posture while singing or speaking helps to ensure that your vocal cords are properly aligned and functioning correctly.
- Breathing: Taking deep breaths and exhaling fully helps to provide the necessary airflow for singing or speaking.
- Pacing: Avoiding speaking or singing too loudly or too often can help prevent overuse and strain on the vocal cords.
- Rest: Giving your voice time to rest and recover is essential to prevent hoarseness and maintain vocal health.
By incorporating these good vocal habits into your daily routine, you can help prevent hoarseness and protect your voice.
Avoiding Irritants
To prevent hoarse voice, it is important to avoid certain irritants that can cause or worsen the condition. Here are some of the most common irritants to watch out for:
- Smoking: Smoking is one of the most significant irritants for the vocal cords. It can cause inflammation, narrowing of the blood vessels, and reduce the amount of oxygen that reaches the vocal cords. Quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do to prevent hoarse voice.
- Alcohol: Drinking alcohol can also irritate the vocal cords and cause inflammation. Limiting alcohol consumption can help prevent hoarse voice.
- Caffeine: Caffeine is a stimulant that can cause dehydration, which can lead to hoarse voice. Limiting caffeine intake can help prevent this.
- Pollution: Exposure to pollution, such as car exhaust or industrial smoke, can irritate the vocal cords and cause hoarse voice. Wearing a mask can help protect against pollution.
- Dust: Dust from construction sites, renovation projects, or sandstorms can also irritate the vocal cords and cause hoarse voice. Wearing a mask can help protect against dust.
- Dry air: Dry air can cause the vocal cords to become dry and irritated, leading to hoarse voice. Using a humidifier or taking steam therapy can help prevent this.
By avoiding these irritants, you can help prevent hoarse voice and keep your vocal cords healthy.
Proper Hydration
Proper hydration is an essential aspect of preventing hoarse voice. The vocal cords are comprised of soft tissues that require moisture to function correctly. Dehydration can cause the vocal cords to become dry, irritated, and inflamed, leading to hoarseness. Therefore, it is crucial to stay adequately hydrated to maintain healthy vocal cords.
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day is the best way to ensure proper hydration. Aim for at least eight glasses of water daily, and avoid sugary drinks, caffeine, and alcohol, as they can contribute to dehydration.
In addition to water, other fluids such as herbal tea, soup, and fruit juice can also help maintain hydration levels. However, it is essential to avoid drinks that contain excessive amounts of sugar or citrus, as they can irritate the vocal cords and worsen hoarseness.
Furthermore, staying hydrated can also help to maintain overall health, which is crucial in preventing hoarse voice. A healthy immune system can help to fight off infections that can cause hoarseness, such as laryngitis or vocal nodules.
Overall, proper hydration is a simple yet effective way to prevent hoarse voice. By drinking enough water and avoiding dehydrating beverages, individuals can keep their vocal cords healthy and reduce the risk of developing hoarseness.
Complications of Hoarse Voice
Acute Laryngitis
Acute laryngitis is a common complication of hoarse voice. It is characterized by inflammation of the vocal cords, resulting in swelling and irritation. This condition can be caused by a variety of factors, including viral infections, excessive shouting or talking, smoking, and acid reflux.
Symptoms of acute laryngitis may include hoarseness, loss of voice, throat clearing, cough, and discomfort when speaking or swallowing. In some cases, the symptoms may be severe enough to require medical attention.
Treatment for acute laryngitis typically involves resting the voice, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding irritants such as smoking and acidic foods. Over-the-counter pain relievers may also be recommended to help alleviate discomfort. In more severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe medication to reduce inflammation and alleviate symptoms.
If left untreated, acute laryngitis can lead to more serious complications, such as chronic laryngitis or vocal cord paralysis. Therefore, it is important to seek medical attention if you experience hoarseness or other symptoms of acute laryngitis that persist for an extended period of time.
Chronic Laryngitis
Chronic laryngitis is a condition in which the larynx becomes inflamed and irritated, leading to hoarseness of the voice. This condition can last for several weeks or even months, and if left untreated, it can lead to complications such as vocal cord paralysis, chronic cough, and respiratory infections.
Symptoms of chronic laryngitis include:
- Persistent hoarseness or loss of voice
- Sore throat
- Cough
- Difficulty swallowing
- Pain or discomfort in the neck or chest
Causes of chronic laryngitis include:
- Repeated episodes of acute laryngitis
- Gastric reflux disease (GERD)
- Smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke
- Exposure to air pollution or chemical irritants
- Overuse or misuse of the voice
Treatment for chronic laryngitis may include:
- Resting the voice
- Avoiding irritants such as smoking or pollution
- Taking medications to reduce inflammation or treat underlying conditions such as GERD
- Engaging in speech therapy to improve vocal habits and techniques
- In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to remove scar tissue or repair damage to the vocal cords.
It is important to seek medical attention if hoarseness persists for several weeks or if there are other accompanying symptoms such as pain or difficulty swallowing. Chronic laryngitis can lead to complications if left untreated, so early diagnosis and treatment are crucial.
Vocal Cord Paralysis
Vocal cord paralysis is a complication that can occur as a result of hoarse voice. It is a condition where one or both of the vocal cords do not move properly, leading to voice changes, hoarseness, and other vocal problems. The vocal cords are responsible for producing sound when we speak or sing, and any abnormality in their movement can cause problems with the voice.
Vocal cord paralysis can be caused by a variety of factors, including nerve damage, viral infections, and autoimmune disorders. It can also be caused by a tumor or growth in the vocal cord area. The condition can be temporary or permanent, depending on the underlying cause and the severity of the paralysis.
Symptoms of vocal cord paralysis include hoarseness, loss of voice, and difficulty speaking or singing. In some cases, the voice may become very soft or breathy, or it may be difficult to project the voice. The symptoms can vary in severity and may be worse in the morning or after speaking for an extended period.
Diagnosis of vocal cord paralysis involves a thorough evaluation of the vocal cords using specialized equipment such as a laryngoscope or videostroboscopy. These tests allow the doctor to examine the vocal cords in detail and assess their movement. Other tests such as blood tests, imaging studies, or a referral to an ear, nose, and throat specialist may also be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the paralysis.
Treatment for vocal cord paralysis depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. In some cases, resting the voice and avoiding excessive talking or singing may be enough to allow the vocal cords to heal. In other cases, medications or therapy may be necessary to address any underlying medical conditions. Surgery may also be necessary in some cases to remove a tumor or repair damage to the vocal cords.
It is important to seek medical attention if you experience hoarseness or other vocal problems that persist for an extended period. Early diagnosis and treatment of vocal cord paralysis can help prevent further complications and improve the chances of a full recovery.
When to Seek Medical Attention
Acute Hoarseness
Acute hoarseness refers to a sudden onset of a hoarse or raspy voice that usually lasts for a short period of time, often a few days to a week. It is often caused by a cold, flu, or other viral infections that affect the vocal cords. In some cases, acute hoarseness can also be caused by overuse or strain of the vocal cords, such as from prolonged speaking, singing, or shouting.
Symptoms of acute hoarseness may include:
- A raspy or strained voice
- Reduced vocal volume or hoarseness that worsens with speaking or singing
- Discomfort or pain when speaking or swallowing
- Swelling or inflammation of the vocal cords
If you are experiencing acute hoarseness, it is important to seek medical attention if:
- Your symptoms persist for more than a week
- You experience difficulty swallowing or breathing
- You have a fever or other symptoms of an underlying medical condition
- You have a history of smoking or other lifestyle habits that may affect your vocal health
A healthcare professional can help diagnose the cause of your hoarseness and recommend appropriate treatment options. This may include resting your voice, avoiding irritants, or medication to alleviate any underlying infection or inflammation.
Persistent Hoarseness
If you have been experiencing hoarseness for an extended period of time, it may be necessary to seek medical attention. Persistent hoarseness can be a sign of an underlying condition that requires treatment. It is important to note that hoarseness that lasts for less than two weeks is typically not a cause for concern. However, if your hoarseness persists for longer than two weeks, it is recommended that you consult with a healthcare professional.
There are several reasons why hoarseness may persist for an extended period of time. Some of the most common causes include:
- Vocal Cord Nodules: These are small growths that can develop on the vocal cords as a result of repeated vocal strain. They can cause persistent hoarseness and may require medical treatment.
- Laryngitis: This is an inflammation of the larynx, or voice box, that can cause hoarseness. Acute laryngitis is typically caused by a viral infection and typically resolves on its own within a week or two. However, if symptoms persist for longer than two weeks, it may be a sign of a more serious condition, such as chronic laryngitis.
- Acid Reflux: This is a condition in which stomach acid flows back up into the esophagus, causing irritation and inflammation. This can also cause hoarseness, particularly in the morning or after eating.
- Thyroid Problems: An overactive or underactive thyroid gland can cause hoarseness, as well as other symptoms such as weight loss or gain, fatigue, and muscle weakness.
If you are experiencing persistent hoarseness, it is important to see a healthcare professional for an evaluation. They will be able to determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and recommend the appropriate treatment. In some cases, this may involve medication or surgery.
When experiencing hoarseness, it is essential to pay attention to any accompanying symptoms that may provide insight into the underlying cause. The following are some common associated symptoms to watch out for:
- Persistent hoarseness: If hoarseness persists for more than a few days or recurs frequently, it could indicate an underlying issue requiring medical attention.
- Pain or discomfort: If you experience pain or discomfort when speaking or swallowing, it may be a sign of an underlying condition, such as acid reflux or a throat infection.
- Breathy voice: A breathy voice may indicate an issue with the vocal cords or airway, such as asthma or bronchitis.
- Difficulty swallowing: Difficulty swallowing can be a sign of a more severe issue, such as a throat tumor or esophageal stricture.
- Other respiratory symptoms: Hoarseness may be accompanied by other respiratory symptoms, such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath. These symptoms could indicate an underlying condition like bronchitis or pneumonia.
- Fever or chills: If you experience a fever or chills along with hoarseness, it could be a sign of a more severe infection, such as a sore throat or tonsillitis.
It is important to pay attention to any associated symptoms, as they can help identify the underlying cause of hoarseness and guide appropriate treatment. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.
Recap of Key Points
- If hoarseness persists for more than two weeks or worsens, seek medical attention.
- If there is difficulty swallowing or breathing, seek immediate medical attention.
- If there is severe pain or discomfort when speaking or swallowing, seek medical attention.
- If there is a fever, chills, or a sore throat, seek medical attention.
- If there is a history of cancer or other serious medical conditions, seek medical attention.
- If hoarseness is accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing, sore throat, or difficulty swallowing, seek medical attention.
- If hoarseness is accompanied by difficulty breathing, chest pain, or tightness in the neck, seek immediate medical attention.
Importance of Seeking Medical Attention
If you experience hoarseness that persists for more than a few days or is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, shortness of breath, or chest pain, it is important to seek medical attention promptly. These symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical treatment.
Additionally, if your hoarseness is caused by a medical condition such as vocal cord paralysis or nodules, it is important to seek medical attention in order to receive proper treatment and prevent further damage to your vocal cords.
In some cases, hoarseness may be a sign of an underlying medical condition that requires ongoing management, such as acid reflux or thyroid disorders. Seeking medical attention can help identify the underlying cause and provide appropriate treatment to manage the condition and prevent future episodes of hoarseness.
Therefore, if you experience hoarseness that persists or is accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention from a healthcare professional who can provide an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Future Research Directions
Although considerable progress has been made in understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment of hoarse voice, there are still several areas that require further research. These include:
Long-term Effects of Hoarse Voice
More research is needed to understand the long-term effects of hoarse voice on vocal health and overall quality of life. This includes investigating the potential for permanent vocal damage and the development of vocal nodules or polyps.
Impact of Hoarse Voice on Vocal Performance
Further research is also needed to explore the impact of hoarse voice on vocal performance, particularly in professional singers and public speakers. This could involve examining the effects of hoarse voice on vocal range, tone quality, and overall vocal endurance.
Development of New Treatment Methods
There is a need for additional research to develop new and more effective treatment methods for hoarse voice. This could include the development of new medications or therapies to target the underlying causes of hoarse voice, such as acid reflux or vocal nodules.
Prevention of Hoarse Voice
Finally, more research is needed to develop strategies for preventing hoarse voice in the first place. This could involve identifying risk factors and developing targeted interventions to reduce the likelihood of developing hoarse voice, such as practicing good vocal hygiene or avoiding irritants like smoke or pollution.
Overall, continued research in these areas has the potential to improve our understanding of hoarse voice and lead to better treatments and prevention strategies.
FAQs
1. What is a hoarse voice?
A hoarse voice is a condition where the voice sounds breathy, raspy, or strained. It is usually caused by irritation or inflammation of the vocal cords.
2. What are the common causes of a hoarse voice?
The common causes of a hoarse voice include vocal overuse or misuse, viral infections such as the common cold or flu, allergies, acid reflux, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
3. What are the symptoms of a hoarse voice?
The symptoms of a hoarse voice include a raspy or strained voice, loss of voice, and difficulty speaking or singing. The voice may also sound quieter or softer than usual.
4. How is a hoarse voice diagnosed?
A hoarse voice is usually diagnosed by a healthcare professional based on the symptoms described by the patient. In some cases, a laryngoscopy or other diagnostic tests may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of the hoarseness.
5. What is the treatment for a hoarse voice?
The treatment for a hoarse voice depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, self-care measures such as resting the voice, drinking plenty of fluids, and avoiding irritants such as smoke and alcohol can help alleviate the symptoms. In more severe cases, medications or surgery may be necessary.
6. How long does a hoarse voice usually last?
The duration of a hoarse voice depends on the underlying cause. In most cases, a hoarse voice will resolve on its own within a few days to a week. However, if the hoarseness persists for more than a few weeks, it is important to seek medical attention.
7. Is a hoarse voice contagious?
No, a hoarse voice is not contagious. It is usually caused by an irritation or inflammation of the vocal cords, which is not contagious. However, the viral infections that can cause a hoarse voice, such as the common cold or flu, can be contagious.
8. How can I prevent a hoarse voice?
There are several steps you can take to prevent a hoarse voice, including avoiding excessive use or strain on your voice, staying hydrated, avoiding irritants such as smoke and alcohol, and practicing good hygiene to prevent the spread of viral infections.